Choosing between a public and private university is a significant decision that shapes a student’s academic journey. This comprehensive guide will help prospective students navigate the complexities of selecting the right institution, weighing factors such as cost, academic programs, campus culture, and career prospects. Whether you’re drawn to the allure of a prestigious private institution or the practicality of a public university, understanding the key differences is crucial. This article offers valuable insights into the advantages and disadvantages of both public and private universities, empowering students to make informed choices aligned with their individual needs and aspirations. Discover how to effectively compare public and private universities, considering factors like financial aid opportunities, class size, and overall educational experience.
Making the right choice between a public and private university can significantly impact a student’s future. This guide breaks down the essential considerations for prospective students, including tuition fees, admission requirements, and campus resources. Explore the nuances of public versus private education, from the perspective of academic rigor to social environment. By carefully evaluating the characteristics of public and private universities, students can confidently select an institution that best suits their academic goals, personal preferences, and financial circumstances. This article provides a roadmap to navigate the decision-making process, ultimately helping students choose the ideal university setting for a successful and fulfilling college experience.
Cost Comparison and Tuition Fees
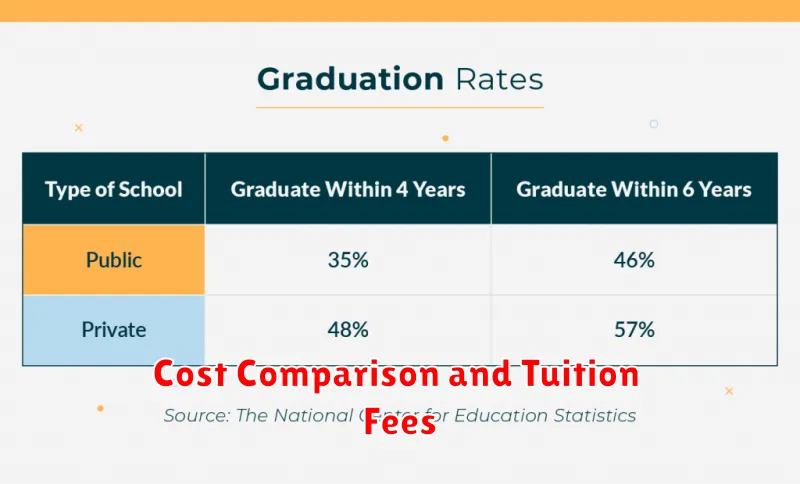
A critical factor in choosing between public and private universities is cost. Tuition fees at private institutions are typically significantly higher than those at public universities. This difference stems from funding sources. Public universities receive substantial government funding, while private universities rely more heavily on tuition, endowments, and donations.
Financial aid availability varies as well. While both public and private universities offer financial aid packages, private institutions often have larger endowments, potentially leading to more generous aid opportunities. However, the higher initial tuition cost at private universities can still result in a higher net price even with aid.
| Cost Factor | Public University | Private University |
|---|---|---|
| Tuition | Lower | Higher |
| Funding Sources | Government Funding | Tuition, Endowments, Donations |
Class Size and Student Support
Class size is a key differentiator between public and private universities. Public universities, due to higher student enrollment, often have larger class sizes, particularly in introductory courses. This can mean less individual attention from professors and fewer opportunities for direct interaction.
Private universities, with their typically smaller student bodies, generally offer smaller classes and a lower student-to-faculty ratio. This translates to more personalized instruction, increased access to professors during office hours, and a greater sense of community within the classroom.
Student support services also vary. While both public and private institutions offer services like academic advising and career counseling, private universities often provide more specialized support and resources due to their smaller size and focus on individual student success. This can include more intensive advising, dedicated writing centers, and readily accessible tutoring programs.
Reputation and Accreditation
Reputation plays a significant role in a university’s perceived value. A strong reputation can impact graduate school admissions and career prospects. Research university rankings and consider alumni outcomes when assessing reputation. However, remember that a prestigious name doesn’t guarantee a perfect fit for every student.
Accreditation ensures that the institution meets certain quality standards. Regional accreditation is generally considered the most prestigious. Verify that both public and private universities under consideration hold proper accreditation. This is crucial for ensuring your degree is recognized and respected.
Look into program-specific accreditation if you have a particular field of study in mind. For example, business schools often seek accreditation from the AACSB, while engineering programs might seek ABET accreditation. Specialized accreditation signals a high-quality program within a specific discipline.
Research vs Teaching Focus
A key differentiator between public and private universities often lies in their primary focus: research or teaching. Public universities, often larger institutions, frequently prioritize research. Faculty members are often engaged in extensive research projects, seeking grants and publishing scholarly work. While teaching remains a core component, the emphasis on research can sometimes translate to larger class sizes, especially in introductory courses, and more interaction with teaching assistants.
Private universities, generally smaller than their public counterparts, often place a stronger emphasis on undergraduate teaching. Smaller class sizes facilitate more direct interaction with professors and a more personalized learning experience. While research is still conducted at many private institutions, the primary focus tends to be on providing a high-quality, student-centered learning environment.
Consider your learning style and priorities when evaluating this distinction. Do you thrive in a research-oriented environment, potentially participating in research projects yourself? Or do you prefer a close-knit learning community with more direct access to professors? Reflecting on these questions can help you determine which type of institution aligns best with your academic goals.
Campus Life and Facilities
Campus life and facilities can differ significantly between public and private universities. Size often plays a major role. Public universities tend to have larger student populations, leading to a more diverse range of clubs, organizations, and events. Private universities, while sometimes smaller, can foster a closer-knit community.
Facilities also vary. While both public and private institutions offer libraries, athletic facilities, and student centers, the scale and resources available can differ. Private universities may have newer or more specialized facilities due to higher tuition fees and endowments. Public universities, while often having extensive facilities, may face higher usage rates due to their larger student body.
Consider your preferences. Do you thrive in a bustling environment with a wide array of options, or do you prefer a smaller, more intimate setting? Reflect on what kind of campus environment best suits your learning style and social needs when making your decision.
Scholarship Opportunities
Financial aid can significantly influence your college choice. Both public and private universities offer a range of scholarship opportunities. Understanding these options is crucial for making an informed decision.
Private universities often have larger endowments, enabling them to provide more substantial merit-based and need-based scholarships. However, don’t discount public universities. They also offer merit-based awards and often have access to state-funded grants.
Researching each institution’s specific scholarship offerings is essential. Explore their websites and contact the financial aid office for details. Remember to consider the scholarship application requirements and deadlines.
What’s Right for Your Goals?
Choosing between a public and private university requires careful consideration of your academic and career aspirations. Each type of institution offers unique advantages that can significantly impact your future.
Think about your intended major. Some public universities are renowned for specific programs, like engineering or agriculture, often due to state funding and research initiatives. Private universities, on the other hand, might offer specialized programs in niche fields, benefiting from smaller class sizes and focused faculty expertise.
Consider your career goals. Are you aiming for a highly specialized profession, or a broader field? Networking opportunities and alumni connections vary between public and private institutions and can be crucial for certain career paths. Research the career services and alumni networks of universities you’re considering.

